How do you diagnose peripheral artery disease?
How Do You Diagnose Peripheral Artery Disease? Exploring Modern Techniques and Expert Insights
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) remains a critical health issue, affecting millions of individuals worldwide by impeding blood flow to the limbs. The journey to diagnosing this condition involves a combination of clinical evaluation, symptom assessment, and sophisticated diagnostic tools. In this article, we will delve into how medical professionals diagnose PAD, highlighting the importance of early detection and the latest advancements in medical technology.
Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease
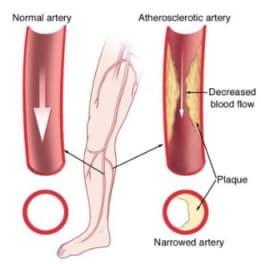
Peripheral artery disease develops when plaque builds up in the arteries that carry blood to the arms and legs, significantly reducing blood flow. Symptoms might include leg pain when walking, leg numbness or weakness, coldness in the lower leg or foot, and sores that do not heal. However, some people with PAD may not exhibit any symptoms, making diagnosis a critical challenge.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a common circulatory problem in which narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to your limbs. When you develop PAD, your extremities — usually your legs — don’t receive enough blood flow to keep up with demand. This causes symptoms, most notably leg pain when walking (claudication).
PAD is often a sign of a more widespread accumulation of fatty deposits in your arteries (atherosclerosis). This condition may be reducing blood flow to your heart and brain, as well as your legs.
What is Peripheral Artery Disease?
Peripheral artery disease is caused by atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaques made up of fat and cholesterol in the artery walls. As the plaques build up, the arteries become narrowed and stiffened, reducing the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the organs and other parts of the body.
Risk Factors for PAD
Understanding the risk factors for PAD is crucial because managing these can help prevent the condition or mitigate its effects if it develops. Key risk factors include:
– Age: PAD is more common in older adults, typically affecting those over 50.
– Smoking: This is a significant risk factor for PAD. Smoking contributes to the constriction and damage of arteries and raises blood pressure.
– Diabetes: High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes cause damage to blood vessels and also lead to narrowed arteries.
– High cholesterol: Excess cholesterol can contribute to plaque buildup and atherosclerosis.
– High blood pressure: This can damage blood vessels and lead to artery stiffening.
– Obesity: Being overweight is a risk factor for developing PAD.
– Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of exercise contributes to a range of conditions, including heart disease and PAD.
– Family history: A family history of PAD, heart disease, or stroke can increase risk.
Symptoms of Peripheral Artery Disease
The most common symptom of PAD is claudication, which is muscle pain or cramping in the legs or arms that is triggered by activity, such as walking, but disappears after a few minutes of rest. The location of the pain depends on the location of the clogged or narrowed artery. Calf pain is the most common location.
The severity of claudication varies widely, from mild discomfort to debilitating pain. Severe claudication can impede walking and other types of physical activity.
Other symptoms of PAD might include:
– Numbness or weakness in the legs
– Brittle toenails
– Coldness in the lower leg or foot, especially when compared with the other side
– Sores on the toes, feet, or legs that won’t heal
– A change in the color of the legs
– Hair loss or slower hair growth on the feet and legs
– Slower growth of toenails
– Shiny skin on the legs
– Erectile dysfunction, especially in men with diabetes
Complications of Peripheral Artery Disease
If left untreated, PAD can lead to severe health problems, including:
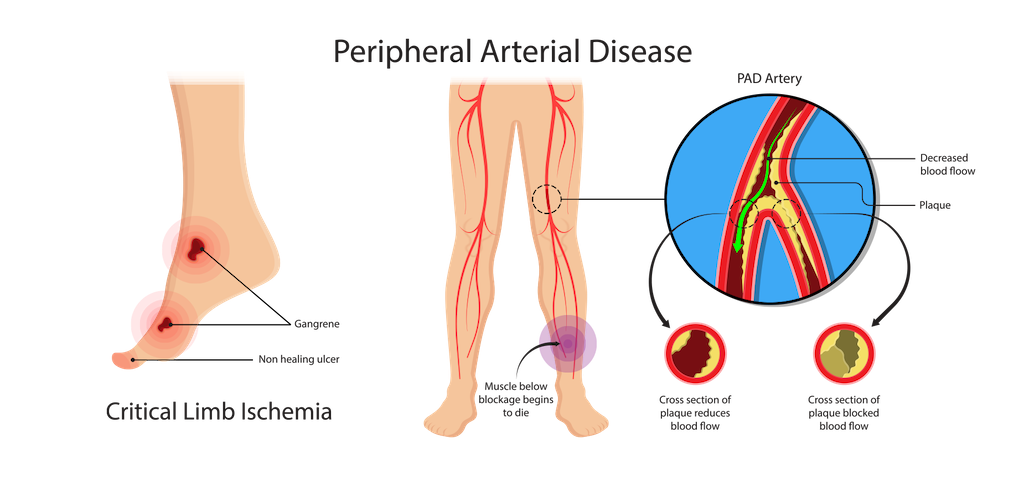
– Critical limb ischemia: This condition begins with open sores that don’t heal, an injury, or an infection of the feet or legs. Critical limb ischemia occurs when such injuries or infections progress and cause tissue death (gangrene), sometimes requiring amputation of the affected limb.
– Stroke and heart attack: The atherosclerosis that causes the signs and symptoms of PAD isn’t limited to your legs. Fat deposits also build up in arteries supplying your heart and brain.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of PAD begins with a physical examination. A key test in diagnosing PAD is the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI), a simple, non-invasive test in which the blood pressure in the ankles is compared with the blood pressure in the arms. Other imaging tests, such as ultrasound, angiography, and MRI, might be used to highlight the state of the arteries.
Treatment for PAD involves lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising, and eating a healthy diet. In more severe cases, medication or surgeries such as angioplasty or bypass surgery might be necessary to open up or reroute blood vessels.
Understanding peripheral artery disease is crucial for early detection and treatment, which can significantly improve the quality of life and reduce the risk of complications such as heart attack or stroke. If you suspect you have symptoms of PAD, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate management.
Initial Consultation and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing PAD often involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Doctors will inquire about any symptoms of leg pain, family history of cardiovascular disease, and risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, and hypertension. During the physical exam, the doctor will check for weak pulses in the legs and feet, signs of poor wound healing, and any changes in the color and temperature of the limbs.
Initial Consultation and Physical Examination for Diagnosing Peripheral Artery Disease
When suspecting Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), the initial consultation and physical examination are crucial first steps in diagnosing the condition. These initial evaluations help healthcare providers not only identify the presence of PAD but also assess the extent and severity of the disease. This stage is vital for developing an effective management plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
The Importance of a Detailed Medical History
The first part of the initial consultation involves taking a detailed medical history. This is a critical component as it helps to identify any symptoms that might be indicative of PAD and any risk factors that could predispose the individual to the disease. During this phase, the healthcare provider will ask questions about:
– Symptoms: Inquiring about symptoms such as leg pain or cramps during walking or exercise, which might relieve upon resting, numbness, weakness, or any changes in the color or temperature of the legs.
-Lifestyle habits: This includes smoking history, exercise routines, and dietary habits.
– Medical history: Discussing existing conditions like diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, or any family history of cardiovascular disease.
– Medications: Understanding any current medications is important, as some can affect blood flow.
Conducting the Physical Examination
Following the discussion of medical history, the physical examination begins, which is pivotal in observing physical signs that suggest PAD. The examination typically includes several key assessments:
– Pulse measurement: The doctor will check for weak or absent pulses in the legs and feet. Pulse points that are routinely examined include the femoral artery in the groin, the popliteal artery behind the knee, and the dorsal pedis and posterior tibial arteries at the foot.
– Inspection of symptoms and signs: The healthcare provider will look for signs of poor circulation such as shiny skin, color changes, slower hair growth, and ulceration.
– Temperature comparison: Comparing the temperature of different parts of the legs and feet can help identify areas where blood flow might be reduced due to narrowed arteries.
– Capillary refill time: This involves pressing on the toenail or the skin to see how quickly the color returns after being blanched (turned white), which can indicate slowed blood flow.
– Ankle-brachial index (ABI): Although usually part of a more detailed diagnostic procedure, a basic ABI might be performed during the physical examination. This involves measuring blood pressure at the ankle and in the arm to compare the two as a ratio, which can indicate reduced blood flow characteristic of PAD.
What Comes After the Initial Examination?
If the history and physical exam suggest PAD, further diagnostic tests will likely be recommended. These could include more detailed blood flow studies, like duplex ultrasonography, computed tomography angiography (CTA), or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) to visualize the blood vessels more clearly and identify specific locations and severity of blockages.
In addition to guiding further diagnostic steps, the initial consultation and physical examination help in the risk stratification of the patient. They provide essential data that can be used to tailor interventions, ranging from lifestyle modifications and medications to potentially more invasive procedures like angioplasty or surgery, depending on the severity of the disease.

The Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) Test
A key diagnostic test for PAD is the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI). This simple, non-invasive test compares the blood pressure in the ankle with the blood pressure in the arm. An ABI ratio of less than 0.90 usually indicates PAD. This test is highly effective as both a screening tool and a diagnostic measure and can be performed in a doctor’s office.
The Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) Test: A Key Diagnostic Tool for Peripheral Artery Disease
The Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) test is a simple, non-invasive, and highly effective diagnostic tool used to detect Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD). This test compares the blood pressure in the ankle with the blood pressure in the arm to assess blood flow and identify any blockages or narrowing in the arteries. The ABI test is not only pivotal for diagnosing PAD but also serves as an indicator of the potential risk for other cardiovascular diseases.
How is the ABI Test Performed?
The ABI test is straightforward and can be performed in a healthcare provider’s office with standard blood pressure equipment and a Doppler ultrasound device. The steps involved in conducting the ABI test include:
1. Preparation: The patient is asked to lie flat and rest for about 5 to 10 minutes before the test begins, as resting blood pressure is needed for accurate measurement.
2. Measuring Arm Blood Pressure: Blood pressure cuffs are placed on both arms, and the higher of the two readings is used for the comparison.
3. Measuring Ankle Blood Pressure: The cuffs are then placed on both ankles, and a Doppler device is used to listen to the blood flow in the ankle as the cuff is inflated and then slowly deflated. The pressure at which the pulse is re-detected in the ankle as the cuff deflates is the ankle systolic pressure.
4. Calculation: The ABI is calculated by dividing the higher of the ankle pressures by the higher of the arm pressures.
Interpreting ABI Values
The results of the ABI test are given as a ratio, which can indicate normal blood flow or the presence of PAD:
– Normal ABI: An ABI ratio of 1.0 to 1.4 suggests normal blood flow without significant blockage.
– Mild to Moderate PAD: An ABI ratio of 0.91 to 0.99 may suggest the presence of mild to moderate PAD.
– Severe PAD: An ABI ratio of 0.90 or less is indicative of severe PAD, suggesting significant blockage.
– Above Normal: An ABI ratio greater than 1.4 may indicate rigid arteries and the need for further cardiovascular evaluation, often seen in patients with diabetes.
Benefits of the ABI Test
The ABI test offers several advantages in the clinical setting:
– Non-invasive and Safe: The ABI test involves no injections, no radiation, and is painless, making it a preferred first-line diagnostic tool.
– Cost-effective: Compared to other imaging tests, the ABI test is relatively inexpensive and can be performed quickly.
– Predictive Value: Besides diagnosing PAD, the ABI can indicate a higher risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes, especially in patients with no symptoms.
Limitations and Considerations
While the ABI test is highly valuable, it has some limitations:
– Calcification of Arteries: In patients with severely calcified arteries, such as those with long-standing diabetes, the arteries may not compress when the cuff is inflated, leading to falsely elevated ABI results.
– Operator Dependency: The accuracy of the ABI test can depend on the experience of the healthcare provider performing the test, especially in interpreting Doppler signals.
Doppler and Ultrasound Imaging
For more detailed imaging, doctors may use Doppler and ultrasound technology. These tools help visualize blood flow in the arteries and identify specific locations of blockages. By assessing the flow of blood, these tests not only confirm the diagnosis of PAD but also help in determining the severity of the disease.
Doppler and Ultrasound Imaging: Essential Tools in Diagnosing Peripheral Artery Disease
Doppler and ultrasound imaging represent critical components in the diagnostic process for Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD). These non-invasive imaging techniques provide valuable insights into the blood flow dynamics within the arteries, particularly those in the lower limbs, helping clinicians assess the presence and extent of arterial blockages or narrowing.
Understanding Doppler and Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound imaging uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. When combined with Doppler technology, it not only shows the structure of blood vessels but also measures the movement of blood through these vessels, allowing for the assessment of both anatomical details and functional blood flow information.
How Doppler and Ultrasound Imaging Work
The procedure typically involves the following steps:
1. Preparation: The patient is positioned comfortably, usually lying down, and the area to be examined is exposed.
2. Application of Gel: A clear gel is applied to the skin over the arteries to be examined. This gel helps the ultrasound probe make secure contact with the skin and eliminates air pockets between the probe and the skin surface, which can interfere with sound waves.
3. Probe Placement: The ultrasound technician or doctor moves the probe (transducer) over the area of interest. The probe emits sound waves that bounce off the blood cells moving through the arteries and return to the probe.
4. Image and Sound Wave Analysis: The ultrasound machine processes the sound waves to create images and sounds that can be interpreted by the physician. The Doppler effect allows the device to capture changes in the frequency of the returning sound waves caused by the movement of blood through the arteries.
5. Assessment of Blood Flow: The Doppler signals provide information about the speed and direction of blood flow. Different colors on the Doppler image may indicate the speed and direction of blood flow, which helps identify areas where blood flow is restricted or blocked.
Advantages of Doppler and Ultrasound Imaging
– Non-invasive and Safe: This method does not require incisions or exposure to ionizing radiation, making it safe for repeated use.
– Real-time Results: Doppler and ultrasound imaging provide real-time pictures of blood flow and arterial structure, allowing immediate assessment.
– Detailed Visualization: These techniques can show the thickness of the arterial wall, the presence of plaques, and the severity of narrowing in the arteries.
Applications in PAD Diagnosis
Doppler and ultrasound imaging are particularly useful for:
– Locating Blockages: Identifying the specific locations of arterial blockages or stenosis.
– Assessing Severity: Evaluating the severity of the blockage and how it affects blood flow.
– Guiding Treatment: Assisting in planning medical or surgical treatments, such as angioplasty or bypass surgery.
– Monitoring Progress: Checking the effectiveness of treatments and monitoring progression of the disease over time.
Limitations
While Doppler and ultrasound imaging are highly effective, certain factors can limit their accuracy:
– Operator Skill: The quality of the imaging and the accuracy of the interpretation can depend heavily on the skill and experience of the operator.
– Physical Limitations: In patients with severe obesity or excessive gas in the intestines, obtaining clear images can be challenging.
– Deep Vessel Imaging: Imaging deep vessels or those obscured by bone can sometimes be difficult.
Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) and Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
In cases where more detailed images are needed, Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) and Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) may be utilized. These advanced imaging techniques provide high-resolution images of the arteries, helping pinpoint where arteries are narrowed or blocked.
Treadmill Exercise Test
For patients who can tolerate physical activity, a treadmill exercise test may be recommended. This test helps assess the severity and functional impact of PAD as patients walk until they feel leg pain. Monitoring the walking distance and time helps evaluate the severity of symptoms and effectiveness of potential treatments.
Blood Tests
Blood tests may not directly diagnose PAD, but they are crucial for assessing risk factors and ruling out other conditions. Typical blood tests might include cholesterol levels, triglycerides, diabetes screening, and markers for inflammation such as C-reactive protein (CRP).
Specialist Consultations
In complex cases, or when the diagnosis is uncertain, referral to a vascular specialist may be necessary. These specialists can perform additional tests, such as angiography, where a contrast dye is injected into the arteries before X-rays are taken to view blood flow and pinpoint any blockages.
FAQs on Diagnosing Peripheral Artery Disease
What is the most common symptom of peripheral artery disease?
The most common symptom of PAD is claudication, which manifests as muscle pain or cramping in the legs or arms that occurs during activities such as walking and subsides with rest.
How reliable is the ankle-brachial index test for diagnosing PAD?
The ABI is highly reliable for diagnosing PAD in symptomatic individuals, especially those with typical symptoms like claudication. It is quick, non-invasive, and cost-effective.
Can peripheral artery disease be diagnosed at home?
While PAD cannot be diagnosed at home, individuals can monitor symptoms and risk factors. Professional medical evaluation is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
Is PAD reversible with medication?
While PAD is not entirely reversible, medications can alleviate symptoms and stop the progression of the disease. Lifestyle changes are also crucial.
How often should someone at risk of PAD be tested?
Individuals at risk of PAD, especially smokers and those with diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, should undergo regular screenings as recommended by their healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Diagnosing peripheral artery disease is crucial for managing the disease and improving quality of life. Through a combination of patient history, physical exams, and both basic and advanced diagnostic tests, healthcare providers can effectively identify and manage this condition. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly reduce the risk of complications, such as heart attack, stroke, and limb amputation. Always consult with a healthcare provider for guidance and the most appropriate testing and management strategies for PAD.
DR. ALOK KUMAR UDIYA
Well-known Interventional Radiologist Dr. ALOK KUMAR UDIYA is currently a consultant at The CARE CHL, an Indore hospital with NABH accreditation. He has a distinguished medical career and has studied at numerous top federal, state, and international superspecialty medical institutes.
He earned his M.B.B.S. from M G M Medical College in Indore and then M.D. in radiodiagnosis from Lady Hardinge Medical College at Delhi University.
Following that, he completed a fellowship in neuro- and vascular interventional radiology at the Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS) in Lucknow, where he gained extensive experience in diagnostic imaging along with hepatobiliary, peripheral vascular, and neurovascular interventions.
The prestigious Institute of the liver and biliary sciences Hospital (ILBS), New Delhi, awarded him a P.D.C.C. (Post Doctoral fellowship) in Hepatobiliary intervention, where he also received further in-depth instruction and advanced training in hepatobiliary and transplant imaging and interventions.
Moreover, he completed a six-month Neuro-Interventional Fellowship (FINR) at the famous University of Zurich, where he received specialized training from Professor Anton Valavanis in the endovascular management of stroke and aneurysm. https://cvicvascular.com/
Contact Us
Contact No. – 099993 78980
Email – dralokudiya@gmail.com
Hospital
Care CHL
Address – AB Rd, near L.I.G Square, RSS Nagar, Indore, Madhya Pradesh 452008
Time – 10am to 5pm
Clinic
Address – 403 Panama Tower Geeta Bhawan Square Near Crown Palace, Indore, Madhya Pradesh
Time – 6pm To 8pm
Read More –
Carotid Stenting – https://interventionradiologyindore.com/carotid-stenting/
What Does Early Signs of Gangrene Look Like? – https://interventionradiologyindore.com/what-does-early-signs-of-gangrene-look-like/
What is the cost of AVM embolization in India? – https://interventionradiologyindore.com/cost-of-avm-embolization-in-india/